Navisys
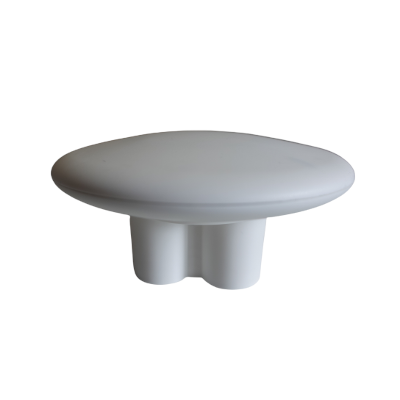
Navisys GR-9029 cm-level accuracy RTK GNSS data logger (Bluetooth BLE V5.2, rechargeable battery, IPX7 waterproof, Includes Data Logging Apps for iOS and Android, Location Sharing Feature for Android)
Navisys GR-9029 cm-level accuracy RTK GNSS data logger (Bluetooth BLE V5.2, rechargeable battery, IPX7 waterproof, Includes Data Logging Apps for iOS and Android, Location Sharing Feature for Android)
Country of Origin: Taiwan
Couldn't load pickup availability
The GR-9029 is a low-cost and user-friendly RTK GNSS data logger that provides cm-level accuracy.

(Data recorded by GR-9029 shown on Google earth)
Prerequisite:
1. IOS or Android device with internet access.
To operate GR-9029, an IOS or Android device is required. Additionally, internet access is required on your device to access a NTRIP caster.
2. NTRIP service.
GR-9029 functions as a RTK rover and requires a NTRIP caster connection via the internet to achieve a cm-level of accuracy.
(Take a look here for the correction service we're suggesting. It could be simpler than you imagine.)
High Accuracy GNSS Data Logging:

In order to use the GR-9029 RTK GNSS data logger, users must first download the free "BluetoothLE_RTK" app from the App Store. Or "BLERTK" app from Google play.
 Users can scan and connect the GR-9029 device via Bluetooth BLE from the settings screen.
Users can scan and connect the GR-9029 device via Bluetooth BLE from the settings screen.
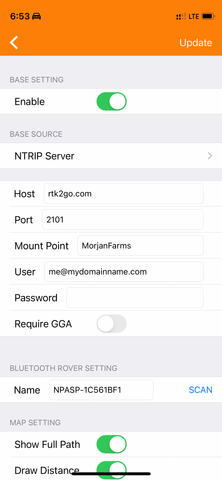
To achieve cm-level accuracy, users need to have their own NTRIP caster service and enter the corresponding settings here.

If your iPhone/iPad has internet access, the app will automatically download RTCM correction data from an internet NTRIP caster and transmit it to the GR-9029 device via Bluetooth BLE.
Using the downloaded RTCM correction data and the data received from GNSS satellites, the GR-9029 device calculates real-time coordinates with cm-level accuracy and sends this data back to the iPhone/iPad using Bluetooth BLE.

Users can view real-time high-accuracy location data on the iPhone/iPad app, and also save it into a log file.
The app creates log files in the native "ubx" format, but users can convert them to other formats (such as GPX, KML, and CSV) within the app as required. These log files can be exported or downloaded for further processing.
Please click on the file to download a sample of the native "ubx" log file recorded by the GR-9029.

I have used the app to convert the sample ubx file to csv, gpx, and kml formats. You can download these files below.
| - GR-9029_sample_log.csv | |
| - GR-9029_sample_log.gpx | |
| - GR-9029_sample_log.kml |

The app defaults to using Google Maps, which offers four different viewing options: Normal, Hybrid, Satellite, and Terrain.
Below are the 2 screenshots of the Satellite view.


GR-9029 can provide centimeter-level accuracy for location data to other applications on the same Android device. (It's important to note that this feature is currently exclusive to Android devices and not available on iOS.)


In addition to data logging and location sharing, the GR-9029 and the BluetoothLE_RTK app can be utilized in other innovative ways, such as cm-level locating and metering.

Technical Specifications
Position Accuracy (RTK baseline up to 20km; 24 hours static):
Horizontal:
RTK: 1 cm+1ppm CEP
SBAS: 1 m CEP
PVT: 1.5 m CEP
Vertical: (result with 1km baseline)
RTK: 1 cm+1ppm R50
Remark: “1 cm+1ppm” means 1 cm + 1 mm per Kilometer for the distance from the RTK rover to the basestation. (For example: when BaseStation and Rover 10 Km apart, the 1 cm+1ppm accuracy is 1cm + 10mm = 2cm)
Velocity Accuracy:
<0.05 m/s (speed) GPS+GLONASS/BDS
<0.3° (heading) GPS+GLONASS/BDS
(50% @ 30 m/s for dynamic operation)
GNSS chip:
u-blox ZED-F9P
Supported GNSS Constellations:
GPS/SBAS/QZSS: (MHz)
L1 C/A (1575.42),
L2C (1227.60)
GLONASS:
L1OF (1602+k*0.5625, k= -7,…,5,6),
L2OF (1246+k*0.4375, k= -7,…,5,6),
Galileo:
E1-B/C (1575.42),
E5b (1207.140)
BeiDou:
B1I (1561.098)
B2I (1207.140)
Supported Augmentation Systems:
QZSS: Support L1S SLAS (Correction data broadcasted on L1)
SBAS: WAAS, EGNOS, MSAS, GAGAN
DGNSS: RTCM 10403.3:
Time Pulse Signal:
0.25Hz...10MHz
RMS: 30ns, 99%: 60ns
Time To First Fix (TTFF) (Autonomous, all at -130dBm):
Hot start: 2sec (GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou)
Aided start: 2sec (GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou)
Cold start: 25sec (GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou)
Sensitivity (GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou):
Acquisition: -148 dBm
Reacquisition: -160 dBm
Tracking & navigation: -167 dBm
Max. Update Rate:
(a. GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou, b. GPS+BeiDoui, c. GPS):
RTK: 8Hz@a, 15Hz@b, 20Hz@c
PVT: 10Hz@a, 25Hz@b, 25Hz@c
RAW: 20Hz@a, 25Hz@b, 25Hz@c
RTK Convergence Time:
(a. GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou, b. GPS+BeiDoui, c. GPS):
<10s@a&b, <30s@c
Depends on atmospheric conditions, baseline length, GNSS antenna, multipath conditions, satellite visibility and geometry
Moving Base RTK Performance:
(a. GPS+Glonass+Galileo+BeiDou, b. GPS+BeiDoui, c. GPS):
Max. update rate: 8Hz@a, 10Hz@b, 10Hz@c
Heading accuracy: 0.4@a,b,c
Protocol Support:
NMEA 0183 up to v 4.11, ASCII
GGA, GLL, GSA, GSV, RMC, VTG, TXT
UBX: u-blox proprietary, binary
RTCM 3.3: binary
Default Settings:
GNGGA output once per second
Rover mode messages: (RTCM)
1001~1012, 1033, 1074, 1075, 1077, 1084, 1085, 1087, 1094, 1095, 1097, 1124, 1125, 1127
Max. Altitude: 50,000 m
Max. Velocity: 500 m/s
Dynamics: < 4g
Bluetooth BLE spec:
BLE transmission distance: 36 meters
Bluetooth version: BLE 5.2
BLE Data: nRF52832
Band : 2.4 GHz ISM
Data Rate: 2 Mbps and 1 Mbps Bluetooth LE
Output Power: Programmable: +4 to -20 dBm in 4 dB steps
Sensitivity: -96 dBm Bluetooth LE 1 Mbps
-89 dBm Bluetooth LE 2 Mbps
RSSI: 1 dB resolution
Link Budget: 100 dB
Built-in battery:
Type: Lithium-ion, 900mAh, Rechargeable
Battery run time : 6 hours
Charging interface: USB Type-C
Charging time: 1.5 hours by 2A charger
Environmental Data
Operating temperature: -40 ~ 85℃ / built-in battery: -10~60℃
Storage temperature: -40 ~ 85℃
Waterproof level: IPX7
Weight:
200g (without pedestal)
246g (with pedestal)
Dimensions:
Dish diameter: 116mm
High: 24.6mm (without pedestal)
High: Diameter: 56.8mm (with pedestal)
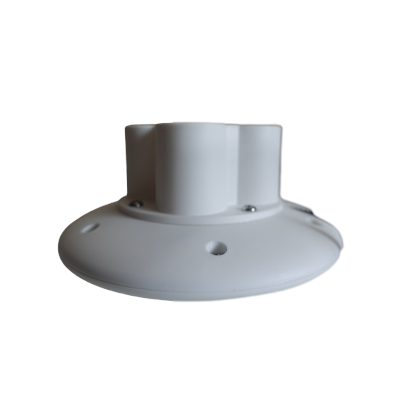
Mounting:
Screw type: M3x8 mm
Fixing screw holes (at the bottom of the disk, covered by pedestal):

Pedestal magnet: Yes
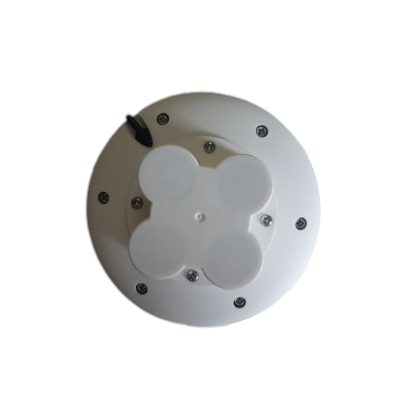
Button:
Power On: short press the button
Power Off: long press the button until the the LED OFF(If Bluetooth BLE disconnected for more than 3 minutes, GR-9029 would power OFF itself. This feature is for energy saving purposes.)
POI tagging: short press the button when in power on state
Package Content:
- GR-9029 RTK GNSS receiver with pedestal x 1
- Usb adapter cable (for charing) x 1
- Download the user guide.
- Download and install the app. Download links located at the bottom of this page.
FAQ:
What is the actual meaning of the “Fixed” status in the BluetoothLE RTK app?
- “FIXED_GPS” fix mode: multi-meter-level accuracy, no RTK
- “FIXED_DGPS” fix mode: meter-level accuracy, no RTK
- “FIXED_FLOATRTK” fix mode: submeter-level accuracy, RTK position stabling
- “FIXED_RTK” fix mode: cm-level accuracy, RTK position stabled
What is the main difference between a RTK GNSS receiver and a traditional GNSS receiver?
The main difference is RTK GNSS takes in the correction stream, but traditional GNSS doesn't.
RTK is short for real time kinematics. A RTK capable GNSS receiver takes in the normal signals from the Global Navigation Satellite Systems along with a correction stream to achieve 1cm positional accuracy. GNSS includes satellites from GPS (USA), GLONASS (Russia), Beidou (China), and Galileo (Europe). On top of these signals an RTK receiver takes in an RTCM correction stream and then calculates your location with 1cm accuracy in real time.
RTK is a technique used to improve the accuracy of a GNSS receiver. Traditional GNSS receivers, like the one in a smartphone, could only determine the position with 2-4 meters (7-13 feet) accuracy. RTK can give you centi-meter accuracy.
Why can RTK GNSS achieve so much better accuracy than standalone GNSS receivers?
GNSS receivers measure how long it takes for a signal to travel from a satellite to the receiver. Transmitted signals travel through the ionosphere and atmosphere and are slowed down and perturbed on the way. For example, travel time on a cloudy day and in clear sky conditions would be different. That is why it is difficult for a standalone receiver to precisely determine its position.
RTK(Real Time Kinematic) technology solves this issue by using correction services. In the RTK method, a user receiver gets correction data from a single base station or from a correction service from the Internet. It then uses this data to eliminate most of the GNSS errors. RTK is based on the principle that the base station and the user receiver are located close together (maximum 40 km or 25 miles apart) and therefore “see” the same errors. For example, since the ionospheric delays are similar for both the user and the reference station, they can be canceled out of the solution, allowing higher accuracy.
Which NTRIP correction services do you recommend for GR-9029?
We highly suggest the GR-9028 Portable RTK Base for your very own NTRIP correction service. It works perfectly with the GR-9029 RTK Rover to give you a complete RTK solution. Set up quickly, flexible NTRIP caster mount point, and easily deploy it near your rovers for super accurate correction data. This will totally revolutionize your RTK needs. See it here and gain control of your RTK solution!
Other than GR-9028, there are still many NTRIP correction services publicly available. Free of charge or by a small fee. They share correction data over the Internet. This technology is called NTRIP. NTRIP is a good option for areas with 3G/4G LTE/5G network coverage and a vast network of NTRIP bases nearby.
Below are the NTRIP correction service sources for your reference:
- Rtk2go (free service, world wide coverage)
- UNAVCO (free service, US coverage)
- A List of Public RTK Base Stations in the U.S.
Product Resources
Official Documents:
User Guides:
YouTube Videos:
Software Downloads:
(To download the app for iOS or Android devices, simply click the link below that corresponds to your device.)
Sample Data Downloads:
How to Articles and Blogs:










